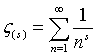Results of the Photon Wave Equation in n dimensions
Only results and calculation formulas are shown on this page. You can find the derivations for them and other useful sources on the bottom of this page.
| 1-D Wave Equation
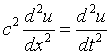 | 2-D Wave Equation
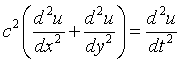 | 3-D Wave Equation
 | Calculation formula |
Eigenfunction
solutions | 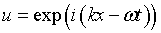
| 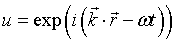
| 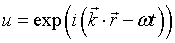
| - |
| Dispersion relation | 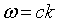
| 
| 
| - |
| Density of states, D(k) | 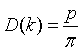
| 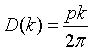
| 
| 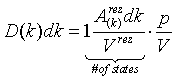
|
| Density of states, D(ω) | 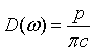
| 
| 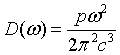
| 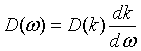
|
| Density of states, D(λ) | 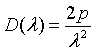
| 
| 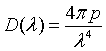
| 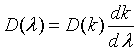
|
| Density of states, D(E) | 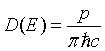
| 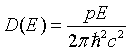
| 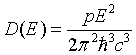
| 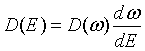
|
| Intensity distribution, I(λ) | 
| 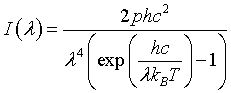
| 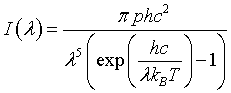
| 
|
| Wien's law | 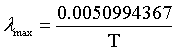
| 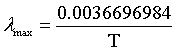
| 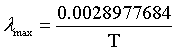
| 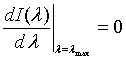
|
| Stefan - Boltzmann law | 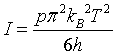
| 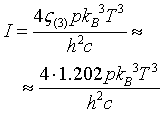
| 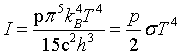
| 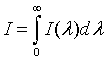
|
| Internal energy distribution, u(λ) | 
| 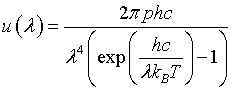
| 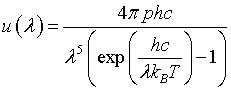
| 
|
| Internal energy | 
| 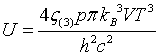
| 
| 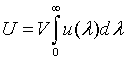
|
| Helmholtz free energy | 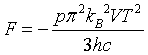
| 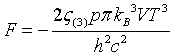
| 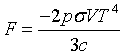
| 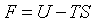
|
| Entropy | 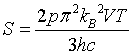
| 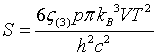
| 
| 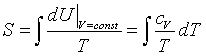
|
| Specific heat | 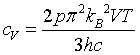
| 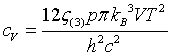
| 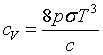
| 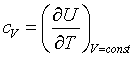
|
| Pressure | 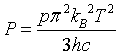
| 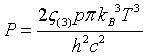
| 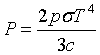
| 
|
|
c = velocity of propagation. Photons: c = 299792458 m/s.
u = wave function.
k = wave number.
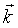 = wave vector. = wave vector.
Ω = the wave's frequency.
p = number of polarizations. Photons: p = 2, Phonons: p = 3.
 = the area of the surface in reciprocal space (k-space) with given k. = the area of the surface in reciprocal space (k-space) with given k.
Vrez = the volume of the brillouin zone in the reciprocal space.
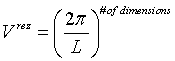 . .
V = volume of our box.
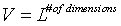 . .
λ = wavelength.
E = energy.
h = Planck constant. h = 6.62606896E-34 Js.
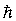 = reduced Planck constant. = reduced Planck constant.
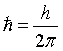 . .
kB = Boltzmann constant. kB = 1.3806504E-23 J/K.
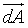 = the vector pointing out of the infinitesimally small area dA. = the vector pointing out of the infinitesimally small area dA.
ΩR = the solid angle of the space. In 3D, ΩR = 4π.
ΩR/2 = the solid angle of the half-space.
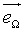 = the unitary vector pointing in the direction specified by Ω. = the unitary vector pointing in the direction specified by Ω.
λmax = the peak wavelength of the intensity.
T = temperature.
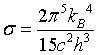 . .
ζ(s) = the Riemann Zeta function.
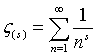 |
How to derive these results
Wikipedia article about the Stefan Boltzmann law
Wikipedia article about Planck's Black Body radiation law
The Bose-Einstein distribution in short
German Wikipedia article containing formulas on Planck's Black Body radiation law
German Wikipedia article about Planck's Black Body radiation law
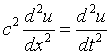
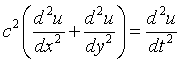

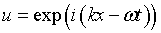
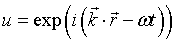
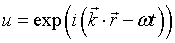
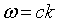


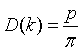
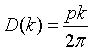

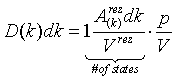
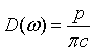

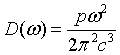
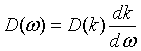
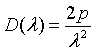

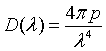
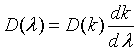
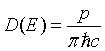
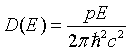
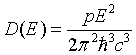
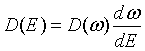

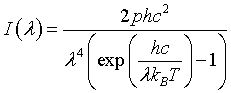
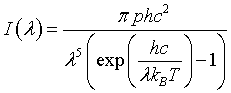

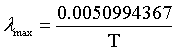
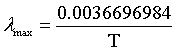
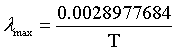
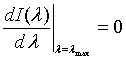
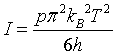
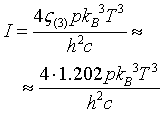
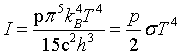
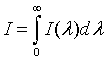

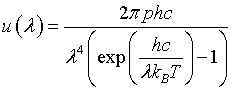
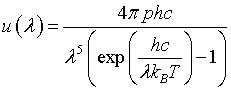


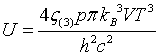

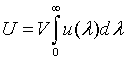
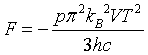
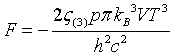
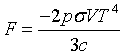
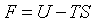
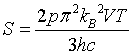
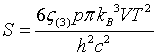

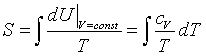
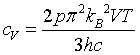
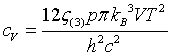
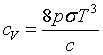
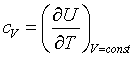
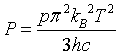
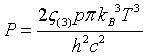
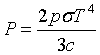

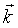 = wave vector.
= wave vector. = the area of the surface in reciprocal space (k-space) with given k.
= the area of the surface in reciprocal space (k-space) with given k.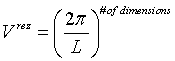 .
.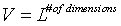 .
.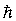 = reduced Planck constant.
= reduced Planck constant. 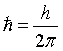 .
.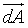 = the vector pointing out of the infinitesimally small area dA.
= the vector pointing out of the infinitesimally small area dA. 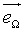 = the unitary vector pointing in the direction specified by Ω.
= the unitary vector pointing in the direction specified by Ω.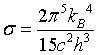 .
.